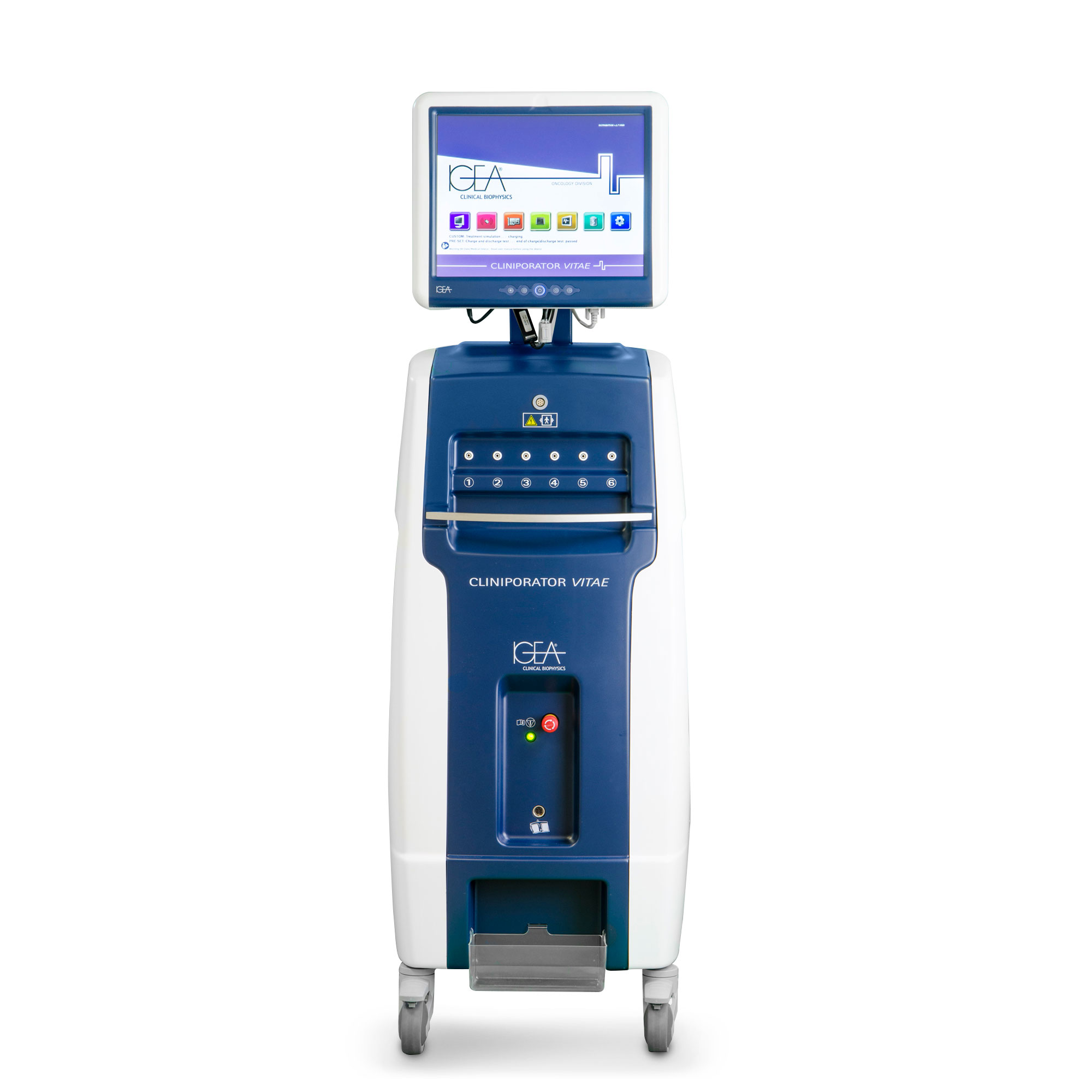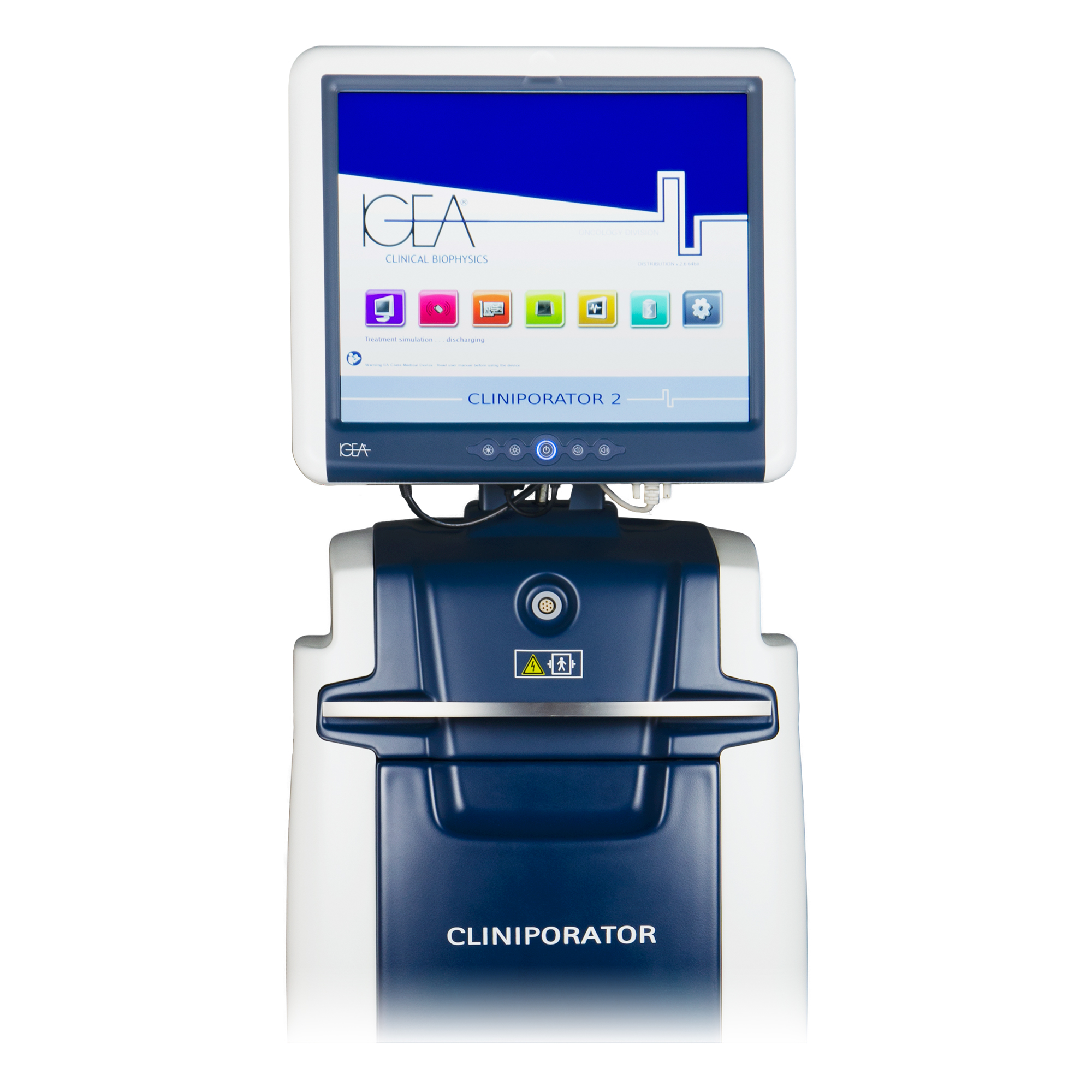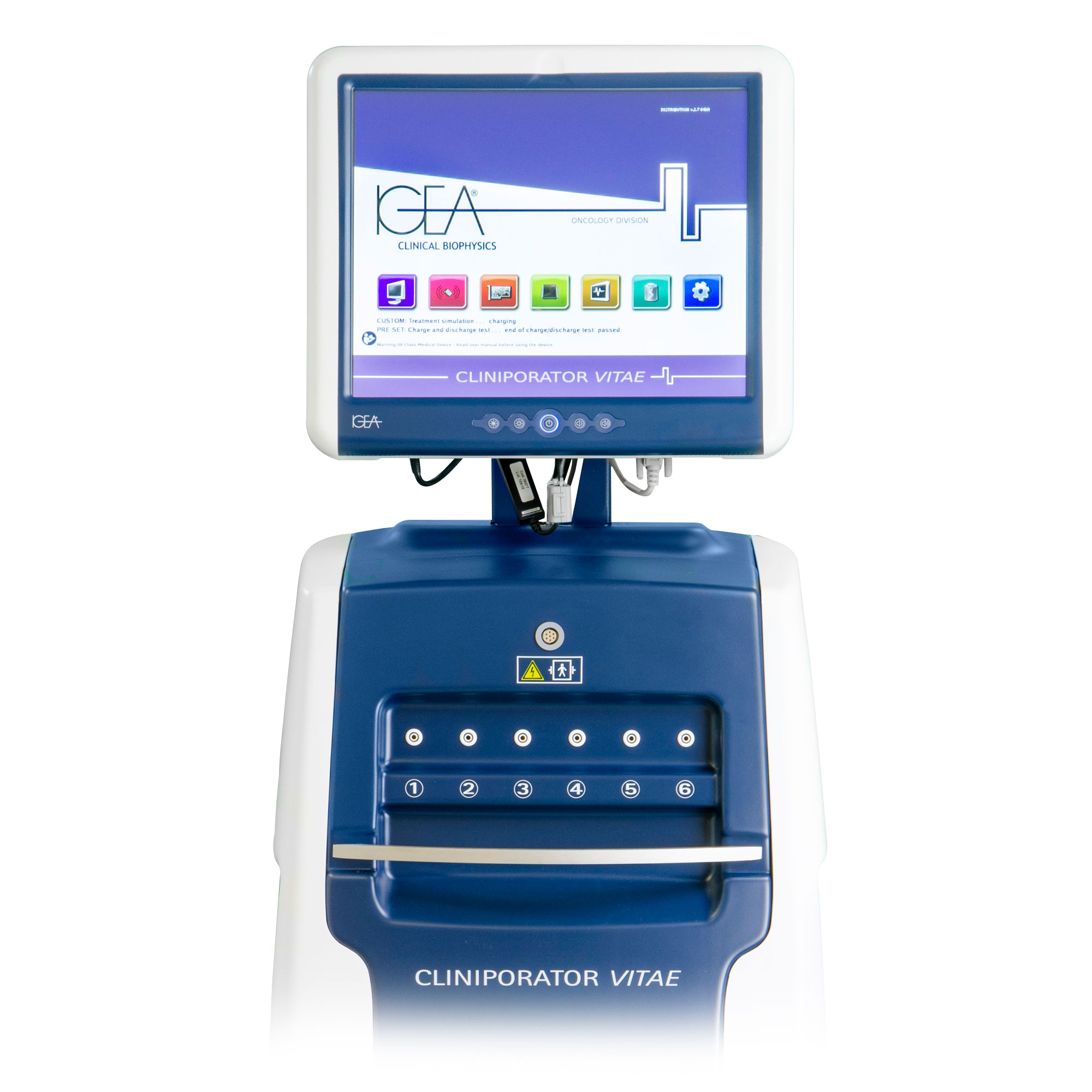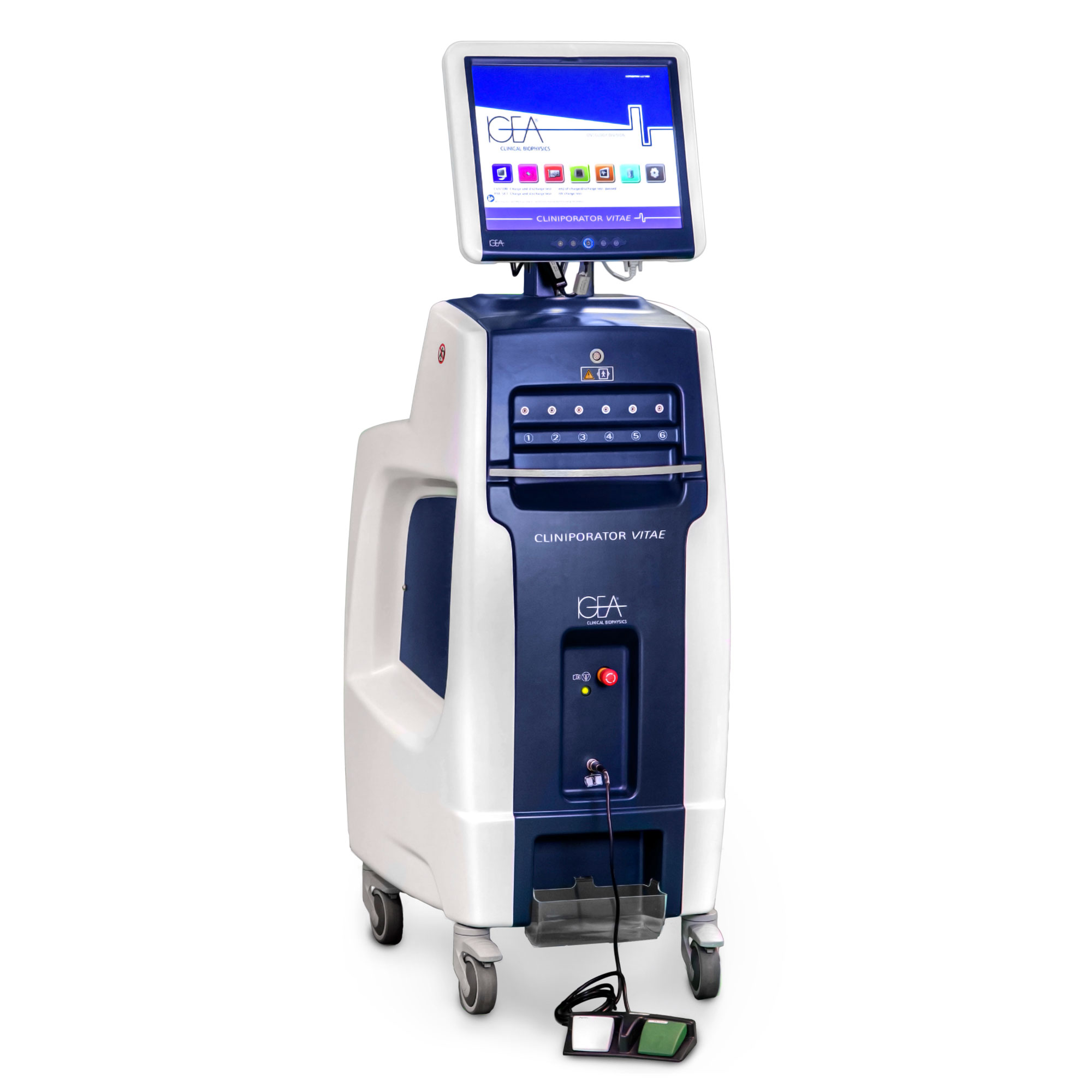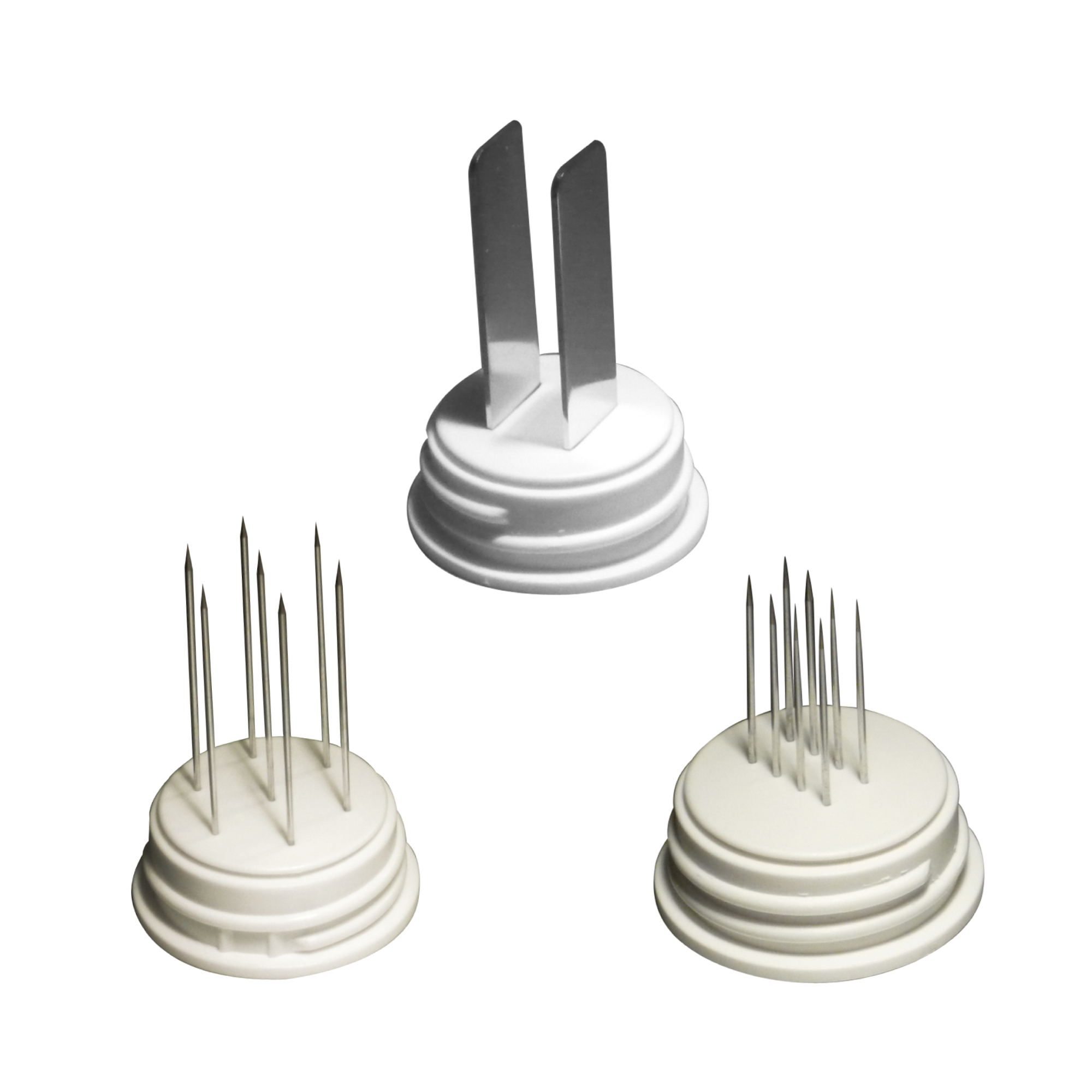
ELECTROCHEMOTHERAPY
ELECTROCHEMOTHERAPY (ECT) IS A MINIMALLY INVASIVE LOCOREGIONAL THERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF SOLID TUMOURS.
Tumour lesions of different origins can be effectively treated with ECT.
It is effective at different disease stages, is generally well tolerated and can be performed subsequently or concurrently with other treatments.
Electrochemotherapy uses the principle of electroporation.
ELECTROPORATION
Electroporation is a physical phenomenon that leads to the permeabilisation of cell membranes through the application of electrical pulses.
It can be reversible when permeabilisation is temporary, or irreversible when it results in cell death following irreparable damage to the cell membrane.
REVERSIBLE ELECTROPORATION
Reversible electroporation allows molecules that would not normally be able to cross the cell membrane due to their properties (water solubility, large size) to enter the cell and perform their function.
Clinical applications of reversible electroporation include:
- Electrochemotherapy
- Electrosclerotherapy
- Electro-gene-transfer